Fullerene C60: A Comprehensive Exploration of its Unique Geometry and Multidisciplinary Potential
Introduction to Fullerene C60 and its Characteristics
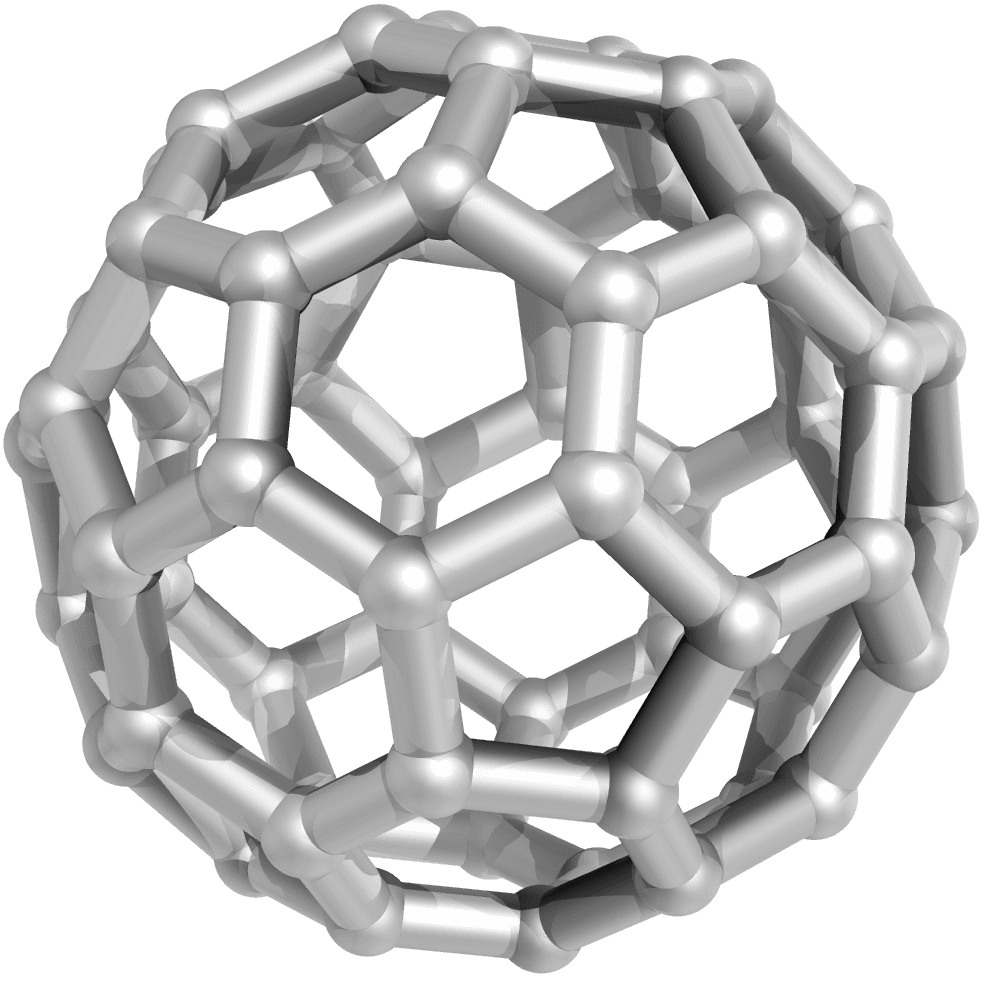
Fullerene C60, stands as a captivating molecule that has commanded scientific intrigue since its discovery in 1985. Resembling the iconic structure of a soccer ball, it belongs to the fullerene family, a group of pure carbon compounds forming closed spherical structures. C60, in particular, boasts a spherical shape with remarkable symmetry, comprising carbon atoms arranged in hexagonal and pentagonal patterns. Notably, it represents the sole allotropic form of carbon entirely soluble in organic solvents, a trait of paramount significance for conducting organic chemistry operations on its carbon framework.
Chemical Properties:
The chemical structure of Fullerene C60 consists of 60 carbon atoms arranged in 12 pentagons and 20 hexagons, forming a sphere with striking icosahedral symmetry. This arrangement of atoms imparts unique and exceptional properties to the molecule. Its carbon-carbon bonds are of uniform length, enhancing its stability and strength.
Physical Properties:
Regarding its physical traits, C60 presents notable features. Its diminutive size, measuring approximately one nanometer in diameter, positions it as the quintessential molecule in the realm of nanoscience and nanotechnology. This nanoscale dimension opens avenues for pioneering applications across a spectrum of fields, spanning from medicine to electronics.

Electronic Properties:
The electronic properties of Fullerene C60 are equally intriguing. Despite its small size, this molecule possesses an electronic band structure that grants it electrical conductivity and the unique ability to accept electrons. Electron-accepting molecules are uncommon in nature and are essential for building molecular electronic devices. This characteristic enables the creation of molecular wires and fully organic, flexible, and cost-effective solar cells.
The derivative of C60, known as C60-PCBM, has become a standard for comparing conversion efficiencies in newly developed solar cells. Its presence in organic solar cell research has revolutionized the landscape, paving the way for more sustainable and accessible technologies in the field of solar energy.
Fullerene C60 stands out not only for its unique chemical structure but also for its extraordinary physical and electronic properties. Its electron-accepting capability positions it as a key molecule in the construction of molecular electronic devices, leading the way to innovative applications in various scientific and technological fields. In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the applications and potential impact of C60 in these fields.

Biological Properties of Fullerene C60 and its Applications
Fullerene C60 shines not only in the realm of nanotechnology and electronics but has also exhibited remarkable biological properties, opening new possibilities in the fields of medicine and molecular biology.
Enzyme Inhibitor and Antibiotic:
C60 has proven to be a potent enzyme inhibitor with hydrophobic pockets in its structure. This has led to significant research in virology, where it has been used to inhibit specific proteases of the HIV virus, consequently showing promising results in the fight against this disease. Furthermore, its capacity as an antibiotic has been studied, exploring its effectiveness against various pathogenic bacteria.
Synthesis of Highly Symmetrical Glycosidic Structures and Prevention of Viral Infections:
C60 has excelled in the synthesis of highly symmetrical glycosidic structures, which have proven effective in preventing viral infections. In the context of emerging viruses such as Ebola, Covid-19, and Dengue, Fullerene C60 and its derivatives have shown the ability to inhibit viral replication and protect host cells. This property has sparked considerable interest in the search for more effective and specific antiviral treatments.
Antioxidant Properties:
Fullerene C60 has revealed exceptional ability to react with and catalytically neutralize reactions with free radicals. Its antioxidant potency is estimated to be approximately 150 times greater than that of vitamin C, making it a promising anti-aging agent and an intercellular “free radical sponge.” This characteristic positions it as a prominent candidate in tissue engineering and tissue repair, where neutralizing free radicals is essential for promoting cellular regeneration and preventing premature aging.


Applications in Photodynamic Therapy:
Derivatives of Fullerene C60 are being employed as photochemical sensitizers in photodynamic therapy, an innovative strategy in cancer treatments. The ability of C60 to absorb light and transfer this energy to surrounding molecular oxygen has led to research aimed at harnessing this property to selectively destroy cancer cells while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues.
In summary, the versatile biological properties of Fullerene C60 make it a fascinating component in medical and biotechnological research. Its potential as an enzyme inhibitor, antibiotic, antiviral agent, antioxidant, and photochemical sensitizer opens the door to a variety of promising therapeutic applications, from preventing viral infections to cancer treatments.
Structural Diversity and Organic Chemistry Applications of Fullerene C60
Fullerenes C60, with their unique and versatile structure, have proven to be the ideal foundation for an impressive structural diversity, driving significant advancements in the field of organic chemistry and opening new possibilities in the synthesis of advanced compounds.
Construction of Dendrimeric Structures and Dendrons:
Fullerenes C60 serve as a starting point for the construction of symmetric dendrimeric structures and asymmetric dendrons with a reduced number of synthetic steps. This process, nearly unattainable with other structures, has revolutionized dendrimer synthesis, expanding molecular design possibilities and surface functionalization.
Modulation of Electronic Properties through Functionalization:
The ability of Fullerene C60 to accept electrons can be modulated through the functionalization of its double bonds. This versatility has led to the design and creation of compounds that find application in advanced electronic devices, from sensors to high-capacity lithium battery components.
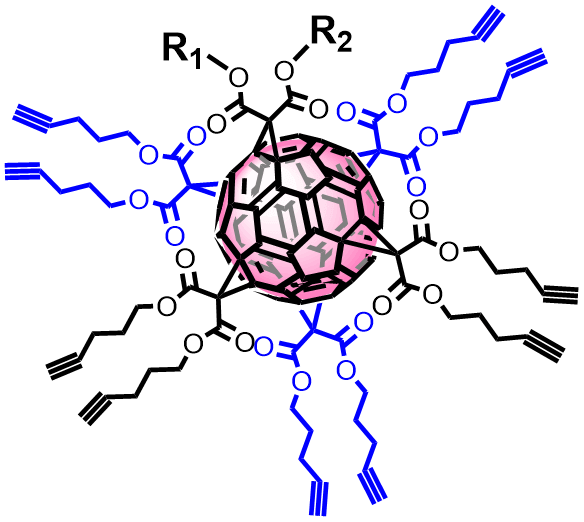
Stability and Sensor Applications:
Fullerenes C60, renowned for their chemical stability, have found applications in the design of highly stable sensors. Their ability to selectively interact with certain compounds has been leveraged to develop precise and reliable detection devices in various fields, from medicine to industry.
High-Performance Polymers and Crosslinking Agents:
In the realm of polymers, Fullerene C60 has been employed to obtain high-performance polymers and as crosslinking agents to enhance the stability of the resulting polymers. These modified polymers find applications in a wide range of industries, from construction to electronics manufacturing.
Lithium Batteries and Anti-Friction Lubrication:
The ability of Fullerene C60 to store lithium has been utilized in the development of high-capacity lithium batteries. Additionally, their spherical structure and hydrophobic nature make them excellent agents for anti-friction lubrication, applied in mechanical systems where efficiency and durability are crucial.

Antitumor Agents and Construction of Self-Assembled Systems:
Fullerenes C60 have demonstrated promising antitumor properties, showcasing their potential in cancer therapy. Their inherent hydrophobicity, combined with the ability to be functionalized to enhance solubility in aqueous media, enables the construction of self-assembled systems in aqueous and organic solvents, opening new opportunities in nanomedicine.
In summary, Fullerene C60 stands out as an exceptional foundation in organic chemistry, providing a flexible framework for developing cutting-edge compounds applicable across a spectrum from electronic devices to nanomedicine. Its modifiable properties and distinctive self-assembly capacity present promising opportunities in pioneering unconventional drug synthesis and the production of advanced materials for pharmacy and biomedicine.